ldpe autoclave reactor process|lyondellbasell ldpe process : factory polymerization process is usually carried out in a continuous mode (tubular or autoclave reactors) at high pressures (1300-3400 atm) and temperatures (50-340 0 C). LDPE exhibits a number of The basic principle of steam sterilization, as accomplished in an autoclave, is to expose each .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Autoclave machines are an efficient and dependable way to sterilize tattoo and nail salon equipment. Autoclaves reduce the danger of infection transfer by submitting reusable tools and equipment to high-pressure saturated steam.Autoclave machines are an efficient and dependable way to sterilize tattoo and nail salon equipment. Autoclaves reduce the danger of infection transfer by submitting reusable tools and equipment to high-pressure saturated steam.
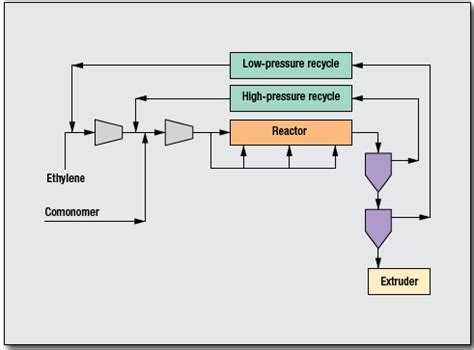
LDPE can be manufactured in either an autoclave reactor or a tubular reactor. The focus of this paper is to discuss the relative characteristics of extrusion coating grade LDPE made using the two processes.offers high-pressure tubular and autoclave process technologies for the production of low .polymerization process is usually carried out in a continuous mode (tubular or autoclave reactors) at high pressures (1300-3400 atm) and temperatures (50-340 0 C). LDPE exhibits a number of The reactor is composed of 4 zones separated by zone baffles. Throughout the zones thermocouples and catalyst injectors were modeled to represent a hypothetical autoclave reactor.
of low density polyethylene (LDPE) and ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers. The Lupotech T process is the leading high pressure tubular reactor technology for the production of LDPE and standard EVA, while Lupotech A is the high-pressure autoclave reactor process technology for the production of specialty LDPE, EVA copolymers with very
A low-density polyethylene (LDPE) production process in an autoclave reactor is used for demonstration. The results show that the proposed iterative method can greatly reduce the computation time .The plastic made at Porvoo, Borealis, LDPE-Plant is low-density polyethylene (LDPE). The process has multiple steps on how the ethylene gas is polymerized using an autoclave reactor. These steps include raising the gas pressure in three steps, cooling the gas, gas
Abstract This work presents how advanced process control can improve energy efficiency of an industrial plant employed to production of low density polyethylene. First, using industrial data, a phenomenological-based model is developed to infer temperature and component concentrations profiles along high-pressure autoclave reactor where polymerization occurs. Then, an . The production of LDPE using the tubular method resulted in the release of excessive heat and remained in the tubular reactor, the polymer gradually deposited onto the surface of the reactor wall during this process [26]. The occurrence of fouling tended to a substantial reduction of heat transfer coefficient and declined the heat transfer .
versalis ldpe resins
While most of the newly installed LDPE/EVA capacities are based on tubular reactors, autoclave reactors are still relevant, especially for producing specialty-grade EVAs. This report reviews the technology and evaluates the process economics for producing EVAs with a high-pressure autoclave reactor process and a high-pressure tubular reactor . It was tentatively concluded, due to lack of favourable comparison to plant data, that CSTR models were unable to fully model the complexities involved in LDPE autoclaves (Wonders et al., 2011). Kolhapure implemented Probability Density Functions (PDF) to model reaction kinetics in a tubular LDPE reactor (Kolhapure et al., 2005). The CFD model . Process Description. Asteasuain et al. developed the current model for LDPE production in a tubular reactor.The model was validated using industrial data consisting of an industrial reactor with a massive length/diameter (L/D) ratio of more than 20,000 (Brandolin et al. 1996).The reactor temperature ranges from 70 °C at the input to 325 °C at the peak, while the .
Advanced mathematical models containing polymerization and decomposition kinetics have proven useful in modeling the LDPE production process. The Polymer Plus model was able to predict polymer properties, production rates, and reactor temperature profiles through a thermodynamic and free radical representation of an autoclave reactor (Bokis et al., 2002).
The aim of the present investigation is the development of a practical model for a high-pressure polyethylene plant. The reactor considered in the present work is an adiabatic slim type autoclave.
LDPE, produced by the high-pressure polymerization of ethylene, is an important commercial product used in film, paper coating, injection molding, and wire/cable insulation. Autoclave is a single source for the design and supply of polyethylene production reactors. Autoclave also supplies associated equipment like Separator Vessels, Catch Pots and Pulsation Bottles for .• Reactor conversation up to 40% • Process and mechanical design up to 400 KTA • Ability to switch from homo-polymers to copolymers • Product from the tubular process is typically higher in molecular weight and has more short chain branches than LDPE from the autoclave process . • Produce LDPE homo-polymers and ethylene vinyl acetateeter ratio of the autoclave reactor is usually in the range of 5 :1-20 :1. There are multiple feed inlets along the axial direction of the autoclave reactor [4-7]. The polymerization process is closely related to the complex flow, temperature, and concentration field distribu-tion inside the autoclave reactor. Studying the polymerization pro-To study runaway behavior in autoclave low-density polyethylene (LDPE) reactors, a kinetic model for a perfectly stirred tank reactor is presented. . Process Safety Progress; CEP Magazine; Books; Join AIChE; aiche.org; AIChE Journal. Volume 42, Issue 10 p. 2911-2925. Reactors, Kinetics, and Catalysis. Runaway phenomena in low-density .
1.1 Process and Reactor Description s T he process here studied is part of a BRASKEM Polyethylene Unit located at city of Santo André, São Paulo state , Bra zil. The plant consists of two identical production lines, both equipped with autoclave reactors . A variety of LDPE grades and/or Ethylene Vi nyl Acetate ( EVA ) To produce low-density polyethylene (LDPE) homopolymers and ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers using the high-pressure free radical process. Large-scale tubular reactors with a capacity in the range of 130,000 tpy–425,000 tpy, as well as stirred autoclave reactors with capacity around 125,000 tpy can be used.• Reactor conversation up to 40% • Process and mechanical design up to 400 KTA • Ability to switch from homo-polymers to copolymers • Product from the tubular process is typically higher in molecular weight and has more short chain branches than LDPE from the autoclave process . • Produce LDPE homo-polymers and ethylene vinyl acetateThe aim of the present work is the development of a practical model for an industrial high-pressure polyethylene plant. The reactor considered in this work is the adiabatic slim type autoclave with four zones for free radical polymerization of ethylene. A fairly comprehensive but realistic model is described that has the ability to predict the temperature at each reaction .
The aim of the present work is the development of a practical model for an industrial high-pressure polyethylene plant. The reactor considered in this work is the adiabatic slim type autoclave with four zones for free radical polymerization of ethylene. A fairly comprehensive but realistic model is described that has the ability to predict the temperature at each reaction . This study addresses a nonlinear model predictive control strategy for the control of multi-zone multi-feed LDPE autoclave reactors. First, a process model is presented to describe the open-loop dynamics of the polymer reactor. Second, the NMPC formulation and the UKF state estimation algorithm are applied to control the temperature and polymer . 1. Introduction. The heat sensitivity of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) production necessitates careful operation. Autoclave reactors commonly used in the production of LDPE operate at temperatures up to 300°C and pressures up to 1500 atm (Kolhapure et al., 2005).When reactor conditions surpass these upper limits, a decomposition event or “decomp” can occur . Various polymers are produced in a continuous stirring reactor under high-pressure conditions, called an autoclave. However, non-ideal mixing is a significant limiting factor in predicting the properties of polymer products and designing industrial-scale reactors owing to a larger time-scale of reactor hydrodynamics (~10 s) compared with that of free radical reaction .
Autoclave LDPE is easy to process, due to its shear thinning behaviour (the viscosity decreases as shear forces increase) and due to its high degree of long chain branching (upon elongation tension stiffening . The autoclave reactor can be considered as a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR), cooling is performed by the ethylene that enters .
The process models selected can be rigorous mechanistic models such as the multi-zone LDPE autoclave reactor model outlined in Section 2, or data-driven nonlinear empirical models, e.g., second order Volterra models [26], neural network based NARMAX models [27], [28], etc. At any sampling instance, the most recent set of measurements are used .
Uhde HPT manufactures full function tested autoclave reactor systems including steel construction design as ready-to-use plants including all accessories like e.g. motors, agitators, bearings, power electrodes, flushing pumps, rupture discs, hydraulic top and bottom cover and clamp handling devices, vibration measurement, various special maintenance tools for reactor .
is the praxis math test hard
is the pre trip inspection test hard
$1,672.00
ldpe autoclave reactor process|lyondellbasell ldpe process